Generation OF Computer
Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation
term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. But nowadays, generation includes both
hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system.
There are a totally five computer generations known till date. Each generation has been discussed in detail along with
their time period, characteristics. We've used approximate dates against each generations which are normally
accepted.
Following are the main five generations of computers
S.N. Generation & Description
1
First Generation
The period of first generation : 1942-1954. Vaccum tube based.
2
Second Generation
The period of second generation : 1952-1964. Transistor based.
3
Third Generation
The period of third generation : 1964-1972. Integrated Circuit based.
4
Fourth Generation
The period of fourth generation : 1972-1990. VLSI microprocessor based.
5
Fifth Generation
The period of fifth generation : 1990-onwards.ULSI microprocessor based
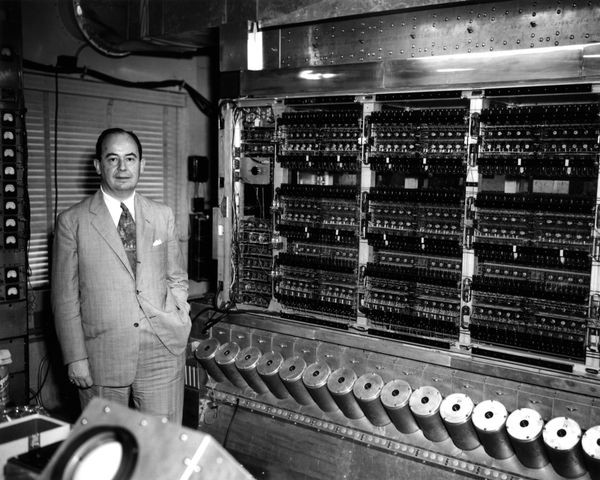
FRIST GENERATION COMPUTER
The computer which were made approximately between 1941 – 1955 (AD). Are classified as the first generation computer.
All the computers which were made during
the first generation had vacuum tubes as their memory and processing device vacuum tube was developed by Lee De Forest in 1908 (A.D.) and
used letter in computer system.
First
generation computer feature
- · Use of vacuum tubes to make circuits.
- ·
Use of magnetic drums.
- ·
Use of machine language and symbols in instructions.
- ·
Very small amount of storage space.
- ·
Use of punch cards as I/O devices.
- ·
Huge in size and poor in mobility.
- ·
Very slow and less reliable output.
- ·
Example: MARK I, ABC, ENIAC etc.
Second generation computer
The computer which were made approximately between 1955-1964 A.D . and having the transistor and diodes
as memory device are classified as the second generation computer transistor
is derived from two device transfer and register. It is the device which is
made of 3 terminal semi-conductor
materials that amplifies the electric single and open or close the electric
circuit. Transistor was invented by three scientist john bardeen , William
Shockley and walter Brattain in 1947 A.D. And won the noble prize in 1956 for
it.
Second generation computer feature
- ·
Use of transistors.
- ·
Magnetic memory and
magnetic storage disks.
- ·
High speed I/O
devices.
- ·
Invention and use of
high level languages such as Fortran and Cobol.
- ·
Reduced size.
- ·
Solution to heat generation.
- ·
Communication by using
telephone line.
- ·
Improvement of speed
and reliability.
- ·
Example: IBM1401, ICL2950/10
Third generation computer
The computer
which were made approximately between 1964-1975 and having IC’s technology
as memory and processing device are classified as third
generation computer. They are constructed on a silicon
chip.
Characteristics of third generation computers include:
- ·
Integrated circuits
instead of individual transistors.
- ·
Smaller, cheaper, more
efficient and faster than second generation computers.
- ·
High-level programming
languages.
- ·
Magnetic storage.
- ·
Example: IBM 360
Series, Univac Ac 9000, ICL1900 etc.
Fourth generation computer
The computer
which were made approximately between 1975 to now and having MICROPROCESSOR as
memory and processing device are
classified as FOURTH generation
computer.
·
The fourth generation computers have
microprocessor-based systems. It uses VLSI (Very Large Scale Integrated)
circuits.
·
They are the cheapest among all the computer generation.
·
The speed, accuracy and reliability of
the computers were improved in fourth generation computers.
·
Many
high-level languages were developed in the fourth generation such as COBOL,
FORTRAN, BASIC, PASCAL and C language.
·
A Further refinement of input/output devices
was developed.
·
Networking between the systems was developed
in fourth generation computer.
FIVETH GENERATION COMPUTER
Definition of: fifth-generation computer. fifth-generation computer.
A computer that exhibits artificial intelligence (AI).
- · ULSI technology.
- ·
Development of true
artificial intelligence.
- ·
Development of Natural
language processing.
- ·
Advancement in
Parallel Processing.
- ·
Advancement in
Superconductor technology.
- ·
More user-friendly
interfaces with multimedia features.
- ·
Availability of very
powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates.



